Focke-Wulf Fw 61 Versuchsmodell-EN
Focke-Wulf Fw 61 Versuchsmodell
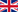
Shown here as a model in scale of 1 : 1 – built by Wilhelm Brinkmann
Professor Henrich Focke, through his development of the Fw 186, and through his work on the C.19 and licence built C.30 autogyros, came to the conclusion that the limitations of autogyros could only be eliminated by an aircraft capable of vertical flight, the helicopter. He and engineer Gerd Achgelis started the design for this helicopter in 1932. A free-flying model, built in 1934 and propelled by a small two-stroke engine, brought the promise of success. Today, the model can be seen in the Deutsches Museum in Munich.
On 9th February 1935, Focke received an order for the building of a prototype, which was designated the Fw 61, however Focke referred to it as the F 61. Roluf Lucht of the technical office of the RLM extended the order for a second aircraft on 19th December 1935. The airframe was based on that of a well-tried training aircraft, the Focke-Wulf Fw 44 Stieglitz.
Using rotor technology licensed from the Cierva Autogiro Company, a single, radial engine drove twin rotors, set on outriggers to the left and right of the fuselage – the counter-rotation of the two rotors solved the problem of torque-reaction as also shown by Louis Bréguet. The small horizontal-axis propeller directly driven by the engine was purely to provide the necessary airflow to cool the engine during low speed or hovering flight- it provided negligible forward thrust.
Only two aircraft were produced. The first prototype, the V 1 D-EBVU, had its first free flight on 26th June 1936 with Ewald Rohlfs at the controls. By spring 1937, the second prototype, V 2 D-EKRA, was completed and flown for its first flight. On 10th May 1937, it accomplished its first autorotation landing with the engine turned off.
Text from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia